
Making of insulator
Insulator
Insulation device, attached to utility poles, made of ceramic or synthetic resin for supporting electric wires for electricity transmission and distribution.
by Bookshelf
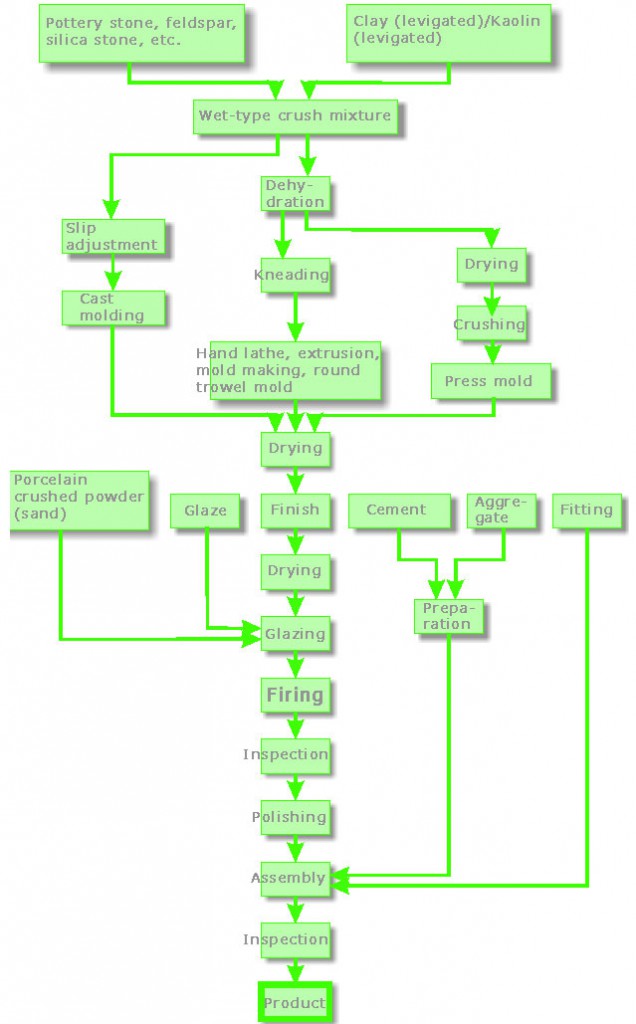
Pottery stone, feldspar stone, etc.

Raw stones, such as pottery stone, feldspar, and silica stones, are finely ground and blended at a certain ratio to which appropriate amounts of clay and water are added, then put in ball mill to turn it into a milky slip.
At our company, the finely crushed raw materials are individually purchased from raw material suppliers.
These pottery stone and feldspar are categorized based on the difference in their chemical composition and are named after the location from which they were mined, such as Amakusa Toseki (Amakusa pottery stone), Tobe Toseki (Tobe pottery stone), and Taishu Choseki (Taishu feldspar).
Levigated clay

Raw materials for porcelain, because they themselves are produced in various forms, cannot be used as is.
Clay, in particular, contains many impurities, and because the particles are not uniform, they must be dissolved in water for levigation to make them even.
Seto city, Aichi Prefecture, because of its history of producing quality clay, has flourished as a city of earthenware.
Ball mill

Pottery stone, feldspar, silica stone, and levigated clay are mixed at a certain ratio and inputted into ball mill with water and ground until they become 50µ.
This condition is called slip.
The ball mill contains 1000 pieces of ceramic balls the size of a tennis ball. When the ball mill rotates, these balls roll inside to crush the materials within.
Deferrization/classification

The slip is put through a sifter to remove coarse particles above #200 (mesh), and iron is removed during this process as well.
Then, it will get sent to an underground tank.
Here, the key is to make sure iron is removed. Because an insulator is a device used to insulate electric wire, if iron is present within the material, it will conduct electricity instead of insulating it.
Membrane Pump

The slip is drawn from the underground tank using a pump and is sent to the filter press.
Filter press

Filter press has multiple layers of cloth (filter) and slip pumped from the pump is accumulated in each layer from which water is filtered.
Cake

The slip dehydrated through the filter press is taken out as a disk-shaped ceramic plate.
This is called a cake.
Rough kneading

The taken out cake is roughly kneaded with a vacuum kneading machine.
Roughly kneaded ceramic comes out in a cylinder-shape which makes it easier to input into the kneading machine for the main knead.
Main kneading

The cylinder-shaped ceramic is, again, kneaded with the vacuum kneading machine to shape it into a material close to the outer diameter of the product in shape.
The kneading machine has a function of kneading the material with even water content and removing the air inside completely.
Cutting

The cylinder-shape ceramic coming out of the kneading machine is automatically cut into a certain length to create the material. This is called a “hoke”.
Round trowel mold

The task of joggling or drilling a blind hole in the center of the hoke.
The metal mold for drilling the hole is called the “round trowel”.
This almost completes the inner shape of the insulator, but it remains rather big due to water content.
Low temperature drying

Round trowel molded hoke is slow dried in a low temperature dry room while maintaining moisture.
Outline finish

Cutting process is performed on the outer shape of hoke dried to a certain extent using an NC lathe and using the hole made by a round trowel mold as a guide.
Main drying

When a product’s outer shape is finished, moisture is completely removed through main drying.
Raw inspection

The products coming out of the main drier are inspected for tears, cracks, etc., which are common occurrences during drying process.
Every single product is checked manually.
Water wiping

Products that pass the inspection are corrected through water wiping for burr.
Marking

Marking printed using paper of “gosu” (red or blue colored glaze) are pasted on the surface of the product.
Glazing

Glaze is applied to the product.
Glaze serves the function of improving product strength and water-resistance as well as dirt-resistance.
Sanding

In order to more firmly attach fixture on the insulator with cement, protrusions are attached on the surface with rough particles.
Kiln loading

Product is loaded onto the cart for firing.
The board on which the product is placed is called the shelf, and the pillar supporting that board is called the piece.
Firing

Fired for 45 hours under 1300℃
Kiln unloading

In a work opposite of kiln loading, the fired product is taken off of the cart in order.
Thermal test

The fired product is plunged in hot water 88℃±3℃ for 15 minutes, then in cold water 8℃±3℃, and these are repeated for expansion and contraction to test durability.
Exterior inspection

Product cracked from the expansion and contraction during the thermal test is inspected.
High frequency test

High frequency is used to perform spark test with internal fissures and iron admixture.
When the iron content is not removed from the process called the “iron removal/classification,” or if iron content is mixed in at a later process, the product will break under the high frequency of this test.
Polishing

For components with strict tolerance, final polish finish is performed.
Shipping

Final visual inspection is performed prior to packaging and boxing.
The insulator, after attaching fittings and enclosing components, etc at a later process, is used as an insulating material for transformers or transmission and distribution facility of electricity.
